How to Handle Difficult Meeting Participants

Introduction
Productive meetings are the cornerstone of successful organizations. They enable teams to brainstorm ideas, resolve issues, and make critical decisions. However, difficult meeting participants can significantly impede the effectiveness of these gatherings. By addressing and managing challenging behaviors, business and team leaders can ensure that their meetings run smoothly and accomplish their intended objectives. In this article, we will cover:
- The common types of difficult meeting participants and their behaviors
- Strategies for handling each type of difficult participant
- Prevention and pre-emptive measures to mitigate potential disruptions
- Managing emotions when dealing with challenging individuals
- The role of the meeting facilitator in handling difficult participants
- When and how to seek additional help for extreme situations
By implementing the techniques and strategies outlined in this article, you can create an environment that fosters productive, engaging, and successful meetings, regardless of the challenges posed by difficult participants.
Types of Difficult Meeting Participants
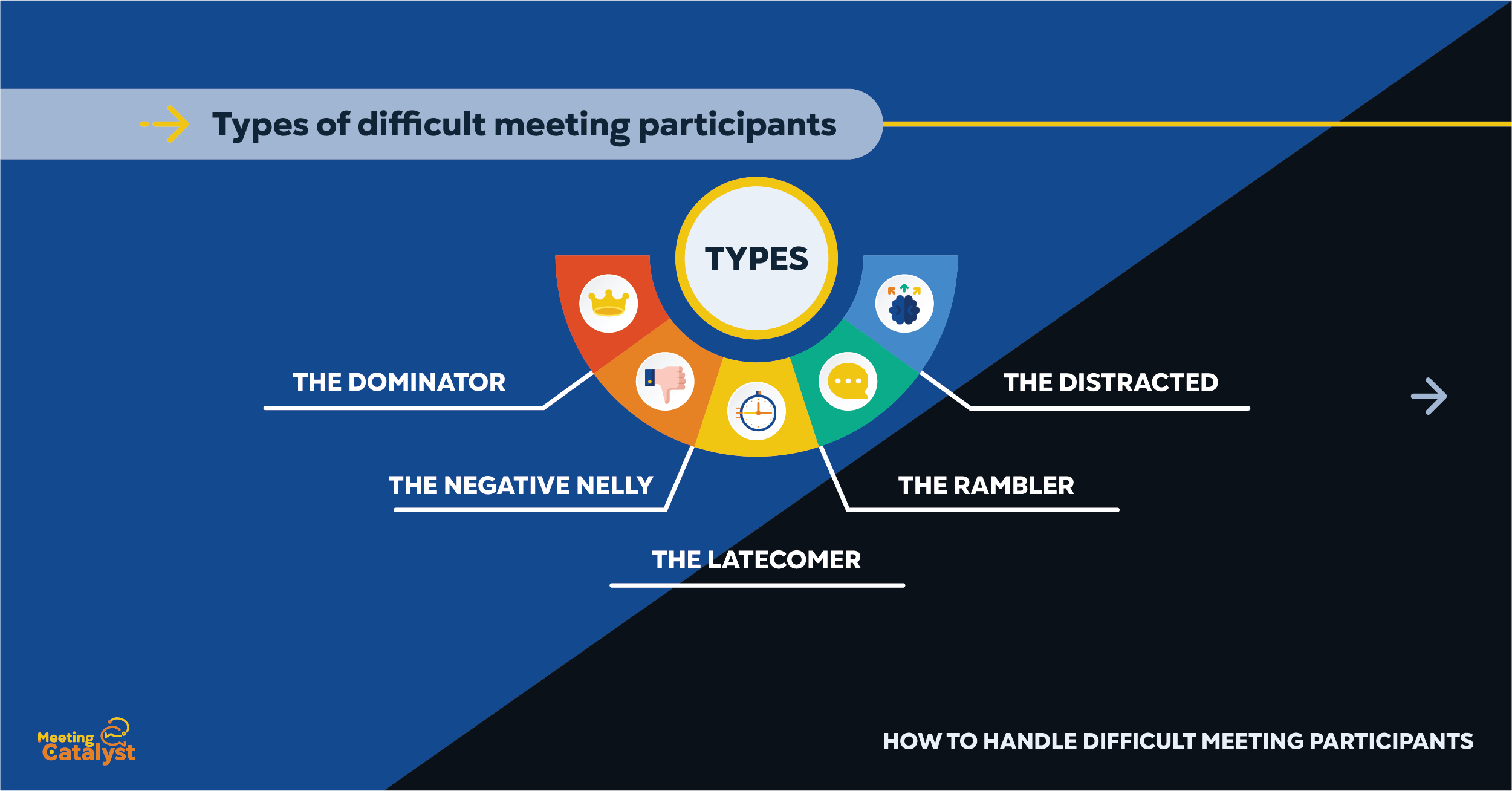
When dealing with difficult meeting participants, it's important to identify the type of behavior they exhibit in order to address it effectively. Here, we will outline common types of challenging participants and provide examples of their behaviors:
The Dominator: This individual tends to monopolize the conversation, interrupt others, and insist on being the center of attention. They may also dismiss or belittle other participants' ideas.
- Example behavior: Constantly interjecting their opinions, even when not relevant to the discussion
The Negative Nelly: This participant is consistently pessimistic, critical, and resistant to new ideas or suggestions. They may have a tendency to shoot down others' contributions without providing constructive feedback.
- Example behavior: Dismissing a colleague's proposal by saying, "That will never work. We tried something similar before, and it failed."
The Distracted: This individual is often preoccupied with their phone, laptop, or other distractions during meetings. Their lack of focus can disrupt the flow of the conversation and hinder group productivity.
- Example behavior: Frequently checking their phone and responding to messages during the meeting, causing them to miss important points and ask for clarification
The Rambler: This participant has a tendency to go off on tangents or provide excessive, irrelevant information. Their long-winded explanations can derail the meeting's focus and waste valuable time.
- Example behavior: Diving into a lengthy personal anecdote that isn't directly related to the topic at hand
The Latecomer: This individual consistently arrives late to meetings, causing disruptions and potentially missing crucial information. Their tardiness may be perceived as disrespectful and can affect the morale of the entire group.
- Example behavior: Arriving 10 minutes late to a meeting and expecting a recap of what they missed
Understanding the various types of difficult meeting participants is the first step in managing their behavior effectively. In the next section, we will discuss strategies for handling each type of challenging participant.
Strategies for Handling Difficult Participants

Effectively managing difficult participants is essential for maintaining productive and focused meetings. In this section, we will provide practical tips and strategies for handling each type of challenging participant:
How to assertively address a Dominator's behavior
- Set clear ground rules for participation at the beginning of the meeting, such as limiting speaking time or taking turns
- Politely interrupt the Dominator and remind them of the ground rules, or suggest that others need an opportunity to speak
- Use body language, such as eye contact and assertive posture, to signal that you expect them to respect the rules
- Encourage quieter participants to share their opinions, demonstrating that all voices are valued
How to redirect a Negative Nelly's negativity
- Ask the Negative Nelly to provide constructive criticism or alternative solutions when they express pessimism
- Reframe negative comments in a positive light by focusing on potential improvements or opportunities
- Acknowledge their concerns while emphasizing the need for a balanced perspective and positive outlook
- Encourage a solution-focused mindset by asking them to brainstorm possible actions to address their concerns
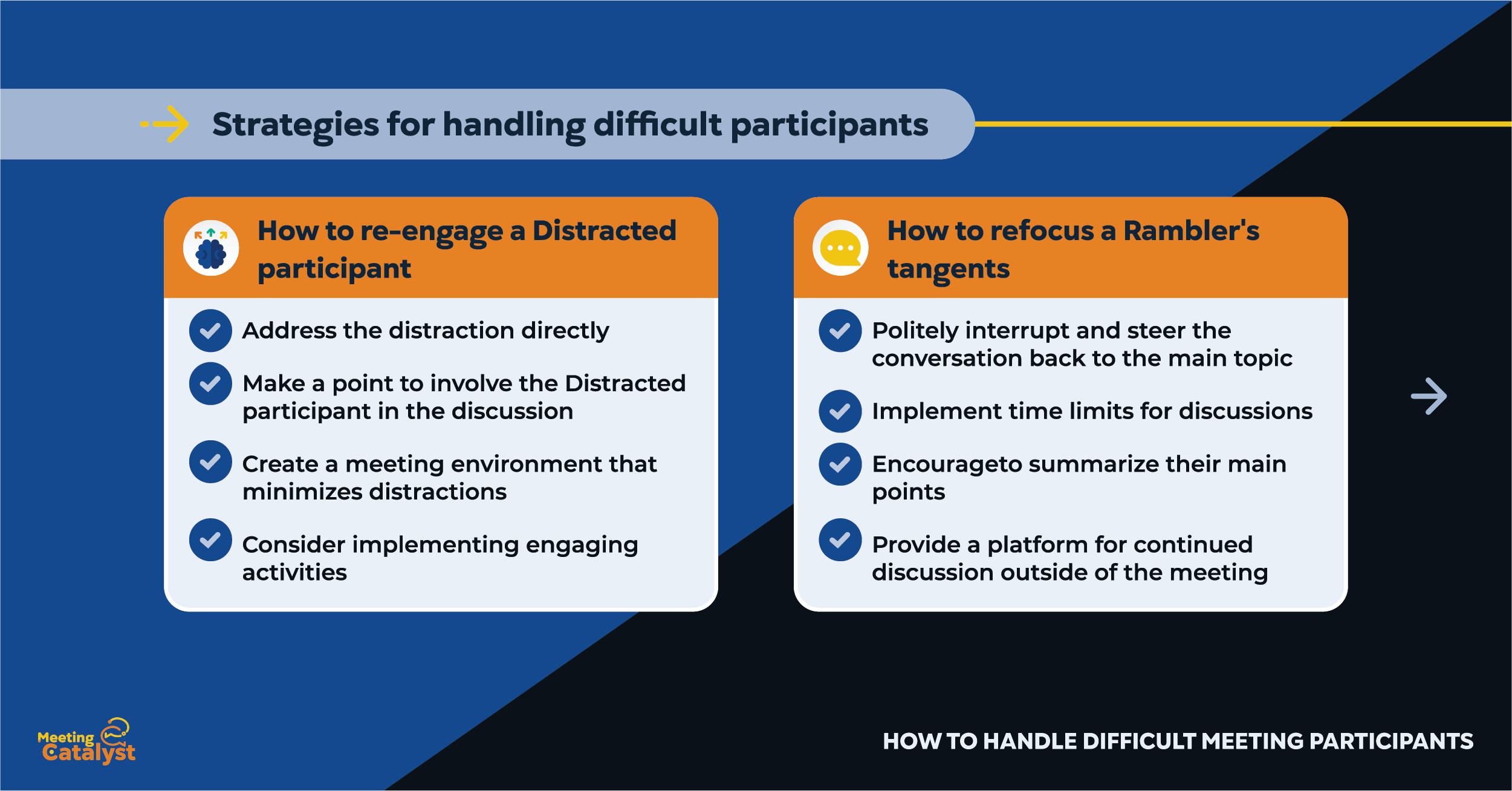
How to re-engage a Distracted participant
- Address the distraction directly by kindly asking the individual to put away their device or focus on the meeting
- Make a point to involve the Distracted participant in the discussion by asking for their input or opinion on a specific topic
- Create a meeting environment that minimizes distractions, such as having a designated device-free zone or setting phones to silent mode
- Consider implementing engaging activities, such as group brainstorming sessions or interactive presentations, to maintain interest and focus
How to refocus a Rambler's tangents
- Politely interrupt the Rambler and steer the conversation back to the main topic, reminding them of the meeting's agenda
- Implement time limits for discussions and remind participants to stay on track
- Encourage the Rambler to summarize their main points and clarify how they relate to the topic at hand
- Provide a platform for continued discussion outside of the meeting, such as a shared online forum or chat, where the Rambler can elaborate on their thoughts
By employing these strategies, you can effectively manage difficult participants and foster a positive, collaborative atmosphere during meetings. In the following sections, we will discuss preventative measures, managing emotions, and the role of the meeting facilitator in addressing challenging behaviors.
Prevention and Pre-Emptive Measures
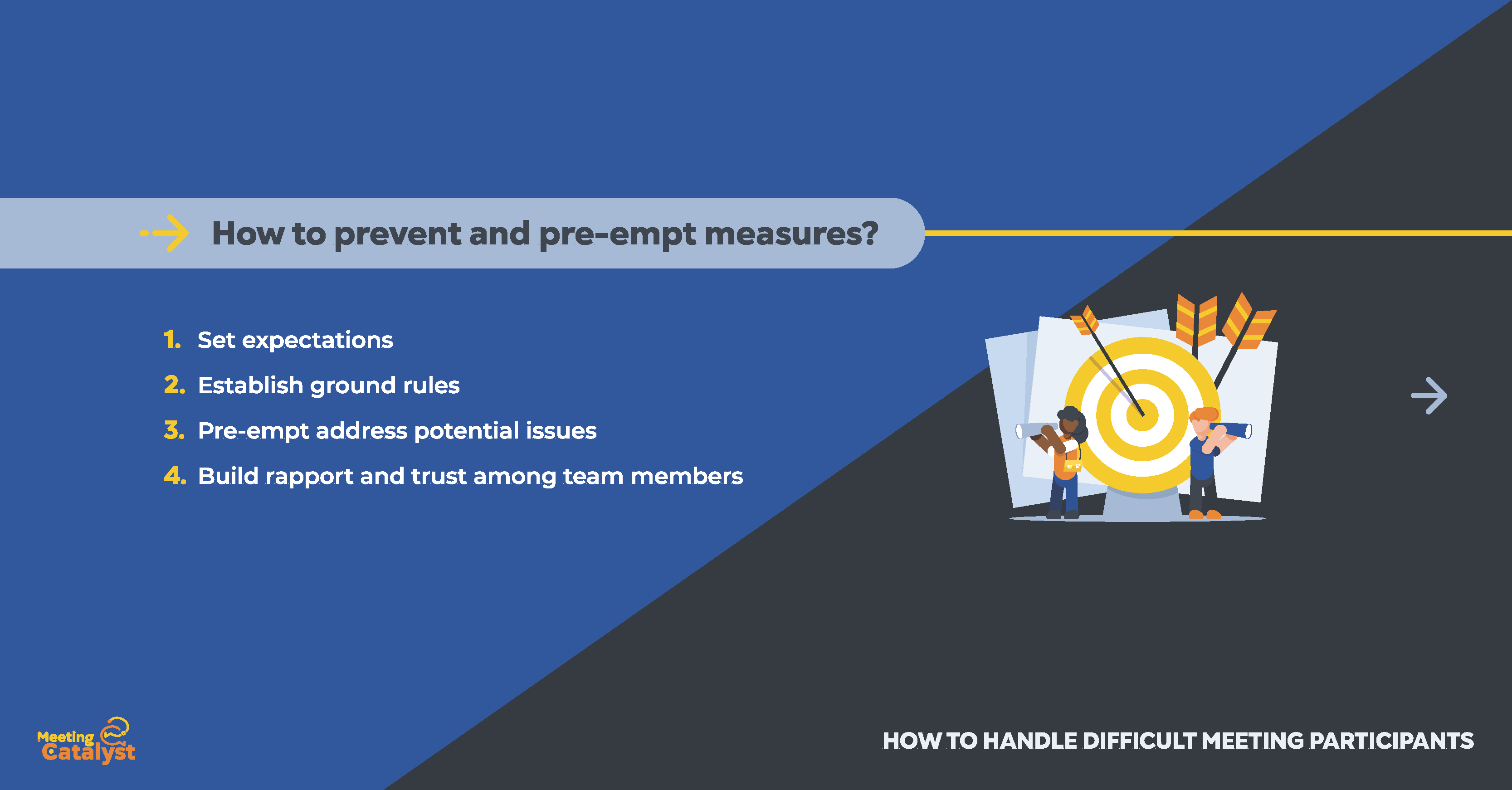
Taking preventative and pre-emptive measures can help mitigate potential issues with difficult meeting participants before they arise. In this section, we will discuss strategies for setting expectations, establishing ground rules, and addressing potential challenges early on:
Setting expectations
- Clearly communicate the meeting's objectives, agenda, and desired outcomes to all participants in advance
- Encourage a culture of respect and professionalism, emphasizing the importance of active listening and constructive feedback
- Foster an environment of inclusivity, ensuring all team members feel valued and comfortable sharing their ideas
Establishing ground rules
- Develop and share a set of ground rules for meetings, covering topics such as punctuality, participation, and device usage
- Ensure all participants are aware of and agree to these rules before the meeting begins
- Consistently enforce the ground rules, holding all participants accountable for their behavior
Pre-emptively addressing potential issues
- Identify any known difficult participants or potential conflicts in advance, and develop strategies to handle these situations
- Address any concerns or issues with individual participants privately, before the meeting, to prevent public confrontation
- Engage team members in the planning process, soliciting feedback on potential challenges and discussing strategies for handling them
Building rapport and trust among team members
- Facilitate team-building activities and informal interactions to foster a sense of camaraderie and mutual respect among team members
- Encourage open communication and transparent feedback channels within the team, creating a safe space for sharing concerns and ideas
- Recognize and celebrate individual and team accomplishments, reinforcing a positive, supportive team culture
By taking a proactive approach and implementing these preventative measures, you can minimize the impact of difficult participants on your meetings and create a more positive, productive environment for all team members. In the following sections, we will explore the importance of managing emotions, the role of the meeting facilitator, and when to seek additional help in addressing difficult participant behaviors.
Dealing with Emotions

Emotions can run high during meetings, especially when dealing with difficult participants. Effectively managing your emotions and those of others is a critical skill for maintaining a productive and respectful atmosphere. In this section, we will discuss strategies for staying calm, managing stress, and addressing emotions in others:
Staying calm under pressure
- Take deep breaths and pause before responding to emotionally charged comments or situations
- Maintain a composed and professional demeanor, even when faced with challenging behaviors
- Focus on the facts and objectives of the meeting, rather than getting caught up in emotional reactions
Managing stress and anxiety
- Utilize stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness exercises or short breaks, to regain composure and mental clarity
- Maintain a balanced perspective, recognizing that one difficult meeting does not define your overall success or abilities
- Seek support from colleagues or mentors, discussing your experiences and learning from their insights and advice
Addressing emotions in others
- Acknowledge the emotions of the difficult participant, showing empathy and understanding for their feelings
- Redirect the conversation to the meeting's objectives and goals, steering the discussion away from emotional triggers
- Encourage open communication and active listening, allowing participants to express their emotions in a constructive manner
Establishing emotional boundaries
- Set clear emotional boundaries, ensuring that you do not absorb the negative emotions of others or allow them to affect your well-being
- Practice self-care and prioritize your mental health, recognizing when you need to step back or seek additional support
- Reinforce the importance of maintaining a professional and respectful atmosphere during meetings, emphasizing that emotional outbursts are not conducive to productivity
By mastering these techniques for dealing with emotions, you will be better equipped to handle difficult meeting participants and maintain a positive, productive meeting environment. In the next sections, we will delve into the role of the meeting facilitator, and when to seek additional help in managing challenging participant behaviors.
The Role of the Meeting Facilitator
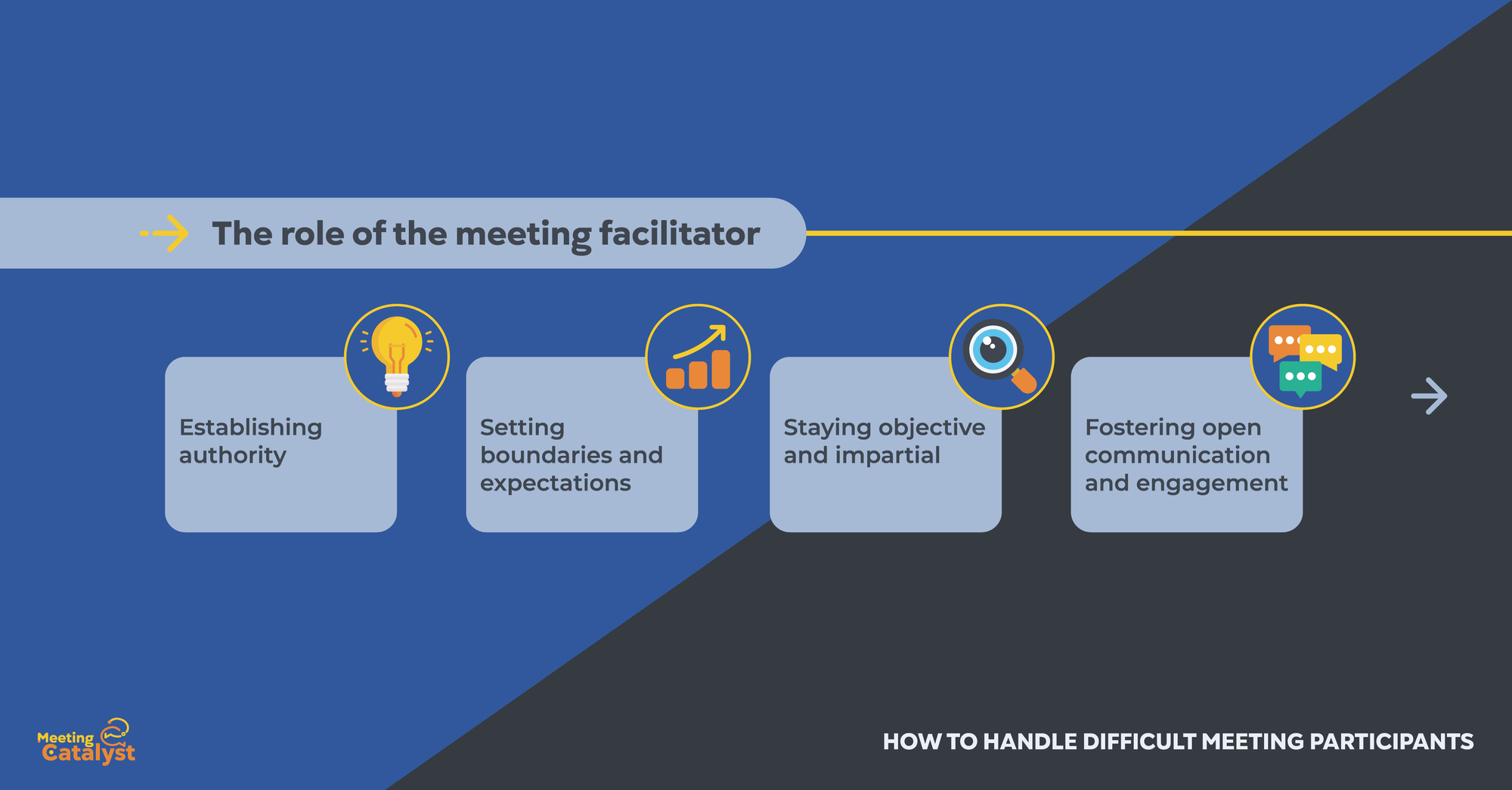
The meeting facilitator plays a crucial role in managing difficult participants and ensuring that meetings run smoothly and effectively. As the person in charge of guiding the meeting, the facilitator must establish authority, set boundaries, and remain objective in addressing challenging behaviors. In this section, we will discuss the essential responsibilities and strategies for effective facilitation in the context of dealing with difficult meeting participants:
Establishing authority
- Begin the meeting by clearly introducing yourself as the facilitator and outlining the meeting's objectives and agenda
- Project confidence and assertiveness, using body language and tone of voice to communicate your leadership role
- Be prepared to intervene when necessary, using your authority to redirect the conversation or address disruptive behaviors
Setting boundaries and expectations
- Establish ground rules for the meeting, including expectations for respectful communication, active listening, and timely participation
- Enforce these boundaries consistently, holding all participants accountable for adhering to the established rules
- Address violations of the boundaries immediately, reinforcing the importance of maintaining a productive and respectful meeting environment
Staying objective and impartial
- Remain neutral when dealing with difficult participants, avoiding the temptation to take sides or become emotionally invested
- Focus on the meeting's objectives and goals, using them as a guide to steer discussions and address disruptive behaviors
- Treat all participants fairly and equally, ensuring that everyone has an opportunity to contribute and voice their opinions
Fostering open communication and engagement
- Encourage open dialogue and active participation from all attendees, inviting input and feedback throughout the meeting
- Utilize inclusive communication techniques, such as paraphrasing, summarizing, and asking open-ended questions
- Create an environment where participants feel comfortable expressing their thoughts and concerns, even when dealing with challenging topics or difficult colleagues
By embracing these key strategies, meeting facilitators can effectively manage difficult participants, maintain a positive meeting atmosphere, and promote productive and collaborative discussions. In the following section, we will explore when it's appropriate to seek additional help in addressing particularly challenging participant behaviors.
When to Seek Additional Help

While meeting facilitators are expected to manage difficult participants effectively, there are situations where it may be necessary to seek additional help or support. Knowing when and how to ask for assistance is crucial to maintaining a safe, respectful, and productive meeting environment. In this section, we will discuss circumstances where it's appropriate to seek additional help and provide guidance on how to do so:
When a participant exhibits aggressive or abusive behavior
- If a participant becomes verbally or physically aggressive, the situation may require intervention from a higher authority, such as a supervisor, HR representative, or security personnel
- Prioritize the safety and well-being of all attendees, taking immediate action to de-escalate the situation and remove the aggressive individual if necessary
When a participant's behavior significantly disrupts the meeting's progress
- If a participant consistently derails the meeting, despite repeated interventions from the facilitator, it may be time to consult with a supervisor or team leader for guidance and support
- Collaborate with colleagues to develop a strategy for addressing the disruptive behavior and ensuring the meeting can proceed effectively
When conflicts between participants cannot be resolved within the meeting
- In cases where interpersonal conflicts persistently disrupt the meeting, it may be necessary to involve a neutral third party, such as a mediator or conflict resolution expert, to help address the issues and find a resolution
- Be prepared to pause the meeting and reconvene at a later time if the conflict cannot be resolved in the moment
When the facilitator feels overwhelmed or unable to effectively manage the situation
- If the facilitator feels they lack the skills, knowledge, or emotional capacity to handle a challenging situation, it's crucial to seek assistance from a supervisor, mentor, or colleague
- Consider participating in professional development opportunities, such as training workshops or coaching sessions, to enhance your facilitation skills and increase your confidence in managing difficult participants
By recognizing when to seek additional help and taking appropriate action, meeting facilitators can better handle complex or challenging situations, ensuring that all participants feel heard and respected while maintaining a productive meeting atmosphere. In the next section, we will conclude the article by summarizing the key takeaways and providing a call-to-action for readers.
Conclusion
In today's fast-paced and dynamic work environment, effectively managing difficult meeting participants is an essential skill for business and team leaders looking to optimize their meetings. By addressing various types of challenging participants, implementing practical strategies, and understanding the role of the meeting facilitator, you can create an environment that fosters collaboration, productivity, and respect.
In this article, we have discussed:
- The common types of difficult meeting participants and their behaviors
- Strategies for handling each type of challenging participant
- The importance of prevention and pre-emptive measures
- How to deal with emotions in difficult meeting situations
- The critical role of the meeting facilitator in managing challenging participants
- When and how to seek additional help when needed
As a business or team leader, you have the power to shape the culture of your meetings and ensure they are productive and engaging for all participants. By implementing the strategies outlined in this article and staying committed to continuous improvement, you can navigate even the most challenging meeting situations with confidence and poise. So, take action today and start transforming your meetings into more effective, efficient, and enjoyable experiences for everyone involved.